NIST Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework: Understanding and Managing Artificial Intelligence Risk
On January 26, 2023, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) released the first version of the Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework (AI RMF). NIST is a US government agency whose mission is “to promote US innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology”. In this context, one of the subjects it works on is artificial intelligence.
The framework provides comprehensive guidance for managing the risks associated with artificial intelligence systems. The NIST AI RMF 1.0 is designed to enable organizations to "minimize the potential negative impacts of AI systems" and identify "opportunities to maximize positive impacts" [1]. In addition to the AI RMF, NIST provides the AI RMF Playbook, which suggests tactical actions to use the framework. Both the NIST AI RMF and AI RMF Playbook are voluntary, not mandatory.
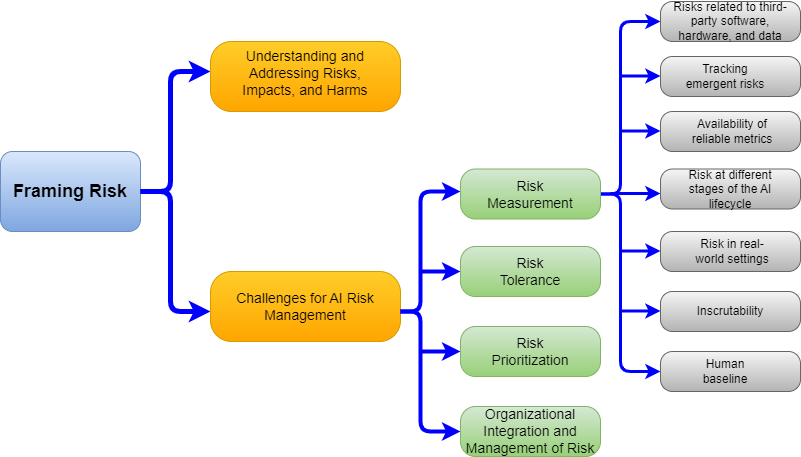
The AI RMF consists of two parts: Foundational Information and Core and Profiles. Framing risks associated with AI is one of the topics covered in the first part. The AI RMF defines risk as "the composite measure of an event's probability of occurring and the magnitude or degree of the consequences of the corresponding event" [1]. The framework then identifies a number of challenges for AI risk management that should be considered while pursuing AI trustworthiness [1]:
The first part also covers the characteristics of trustworthy AI systems. According to the AI RMF, there are seven characteristics that define trustworthy AI [1]:
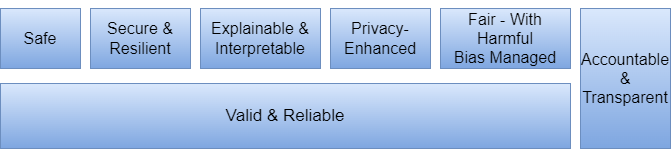
The AI RMF explains each of these characteristics in detail and provides guidance for addressing them.
In the second part, The NIST AI RMF Core provides a framework for managing AI risks and developing trustworthy AI systems. The Core consists of four functions: GOVERN, MAP, MEASURE, and MANAGE. Each function is further broken down into categories and subcategories, which are subdivided into specific actions and outcomes [1].
The GOVERN function is a critical component in AI risk management, which activates other functions and should be continually attended to throughout an AI system's lifespan and the organization's hierarchy [1].
The MAP function builds the context for framing risks and, the information collected while performing it enables organizations to prevent adverse risks and informs critical decisions [1]. Also, it provides a base for MEASURE and MANAGE functions [1].
The MEASURE function analyzes and assesses AI systems for risks and trustworthiness based on the knowledge identified in the MAP function by employing quantitative and qualitative methods [1].
The MANAGE function involves allocating risk resources to mapped and measured risks [1]. It is designed to help organizations manage risks by prioritizing and responding to them.
Writer : Gamze Büşra Kaya
Reference
| [1] | E. Tabassi, “AI Risk Management Framework: AI RMF (1.0),” National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD, 2023. |



